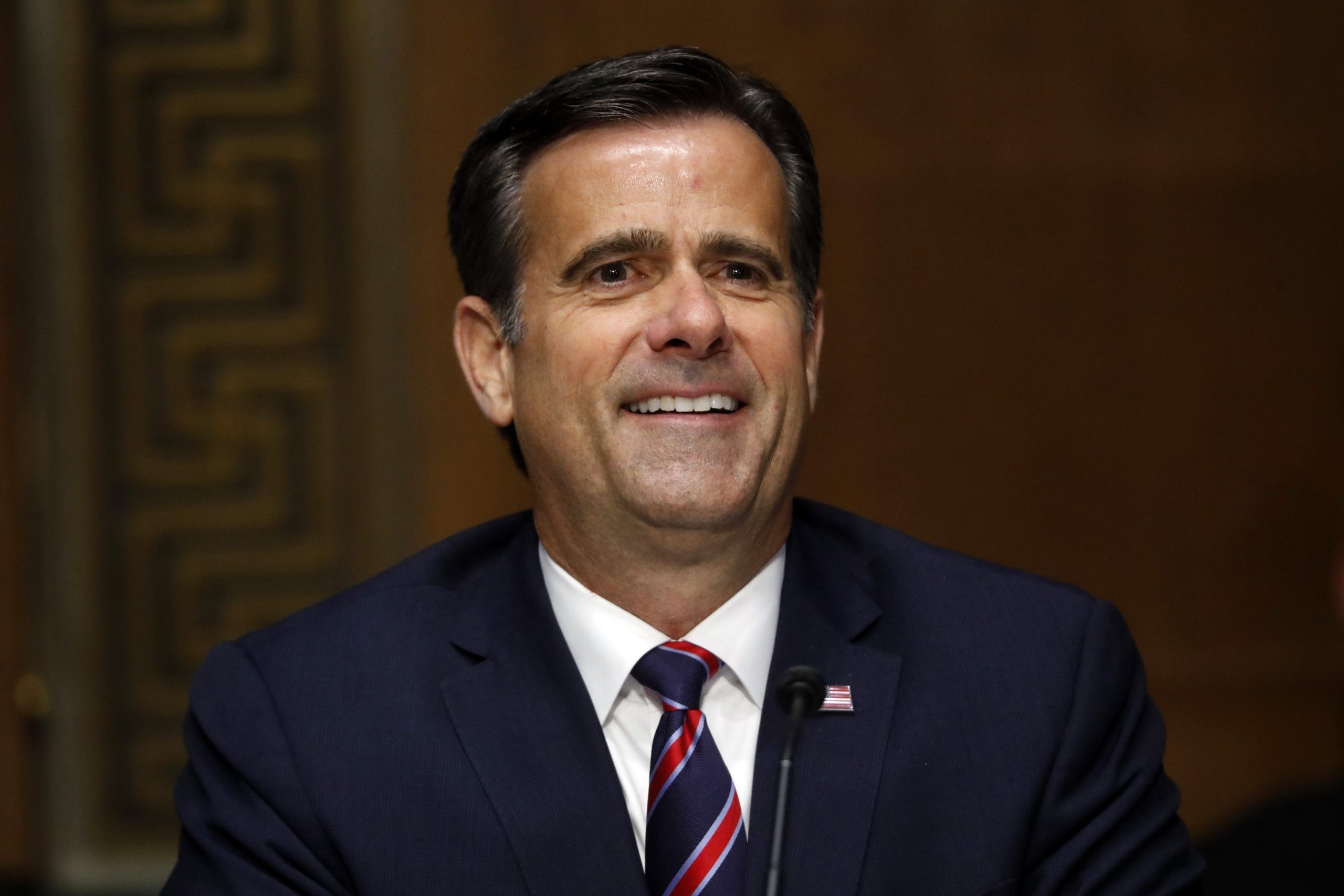
BOSTON — Russia and Iran have obtained U.S. voting registration information, the government’s national intelligence director said at a rare news conference Wednesday night.
John Ratcliffe, the intelligence director, and FBI Director Chris Wray say the U.S. will impose costs on any foreign countries interfering in the 2020 U.S. election.
_____
THIS IS A BREAKING NEWS UPDATE
Democratic voters in at least four battleground states including Florida and Pennsylvania received threatening emails, falsely purporting to be from the far-right group Proud Boys, that warned “we will come after you” if the recipients didn’t vote for President Donald Trump.
The voter-intimidation operation apparently used email addresses obtained from state voter registration lists, which include party affiliation and home addresses and can include email addresses and phone numbers. Those addresses were then used in an apparently widespread targeted spamming operation. The senders claimed they would know which candidate the recipient was voting for in the Nov. 3 election, for which early voting is ongoing.
Federal officials have long warned about the possibility of this type of operation, as such registration lists are not difficult to obtain.
“These emails are meant to intimidate and undermine American voters’ confidence in our elections,” Christopher Krebs, the top election security official at the Department of Homeland Security, tweeted Tuesday night after reports of the emails first surfaced.
He urged voters not to fall for “sensational and unverified claims,” reminding them that ballot secrecy is guaranteed by law in all states. “The last line of defence in election security is you – the American voter.”
A spokesperson at FBI headquarters did not immediately return a phone call seeking comment.
Asked about the emails during an online forum on Wednesday, Pennsylvania Secretary of State Kathy Boockvar said she lacked specific information. “I am aware that they were sent to voters in multiple swing states and we are working closely with the attorney general on these types of things and others,” she said.
Bennett Ragan, the campaign manager of Florida statehouse candidate Kayser Enneking, said he got two of the emails and knew about 10 other people in Gainesville who also got them. Bennett said the home address included in the personalized email he received was not current so he figures the data on him was acquired from the 2018 primary election voter roll.
The emails were sent by a group — its identity unknown — that put considerable time and effort into identifying vulnerable internet servers in several countries including Estonia, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates which they hijacked to send the emails, said security researcher John Scott-Railton, who examined dozens. Voters in Arizona and Alaska also received them, he said.
The Associated Press obtained the personalized email from two Florida voters in different parts of the state.
Scott-Railton, of the Citizen Lab online civil-rights project at the University of Toronto, said the Proud Boys email address that the spammers placed in the email’s sender field was “a flag of convenience.” The true addresses of origin — not readily visible but listed in email headers — were the hijacked servers. The emails reviewed by the AP both appeared to originate from a business in Estonia.
And while the operation was not terribly sophisticated, it may still have been backed by a nation-state. There are documented cases in which Russian agents have sent threatening mail, including to U.S. military spouses. Ukraine has also been hit by email hoaxes suspected to be the work of the Kremlin. Intelligence services like to use such techniques because they don’t bear the stamp of government, thus providing deniability.
“We’ve definitely seen state actors impersonate political figures and factions in the past. It wouldn’t be unheard of for them to do that in this case,” said John Hultquist, director of threat intelligence analysis at the cybersecurity firm FireEye. None of the Russian military hackers indicted by U.S. prosecutors for interfering in the 2016 presidential election on Trump’s behalf have been brought to justice.
“To me this is a canary case. And what it shows is that somebody with obvious malicious intent can get messages that leverage voter registration data in front of the eyeballs of a large number of Americans,” said Scott-Railton. The emails clearly penetrated the spam filters of email providers, he said, though some were likely blocked.
Microsoft and Google, major email providers with top-notch security researchers and tools, did not immediately comment on how many of the spoofed mails may have been sent and what intelligence they may have about the sender’s identity.
“The real question is just how well did this operation cover its tracks,” said Scott-Railton, who worries that the operation might have been a dry run. “Is someone testing a capability that they intend to use on a much larger scale in the future?”
He urged the U.S. government and its allies to be as transparent as possible about what they know about the operation as soon as possible to assure the public that it does not endanger election security.
In a post on the messaging service Telegram, an account that claims to represent the Seattle Proud Boys said the group had no involvement with the emails, calling them a “false flag operation.” President Trump has been criticized for refusing to condemn the far-right group.
Daniel Tokaji, dean of the University of Wisconsin Law School and an expert on voting rights, said he’s afraid we could see more of the type of voter suppression that the intimidation emails attempt — trying to scare people into not voting at all.
Jessica Levinson, a Loyola Law School professor, said the use of voter roll information could make the emails especially frightening. “It puts so much unfair stress and responsibility on the voters and nobody should have to fear for their safety when deciding who to vote for — but that’s exactly the point of voter suppression.”
—-
Associated Press writers Eric Tucker in Washington, D.C., David Klepper in Providence, R.I, and Christina Cassidy in Atlanta contributed to this report.
Frank Bajak And Eric Tucker, The Associated Press